Alexander ERESKOVSKY, Sandrine CHENESSEAU, Christian MARSCHAL (IMBE)
Christel PINAZO (MIO)
Laurent VANBOSTAL (OSU Institut Pytheas)
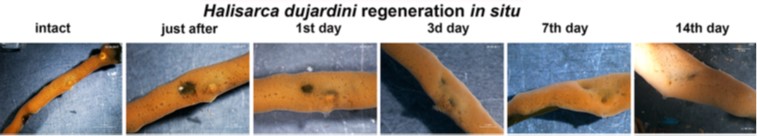
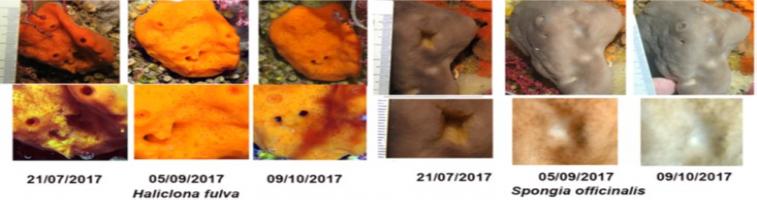
The studied species are sponges of different growth forms that live under different ecological conditions (Haliclona fulva, Aplysina cavernicola, Spongia officinalis, Clathrina clathrus) and are major elements of coralligenous ecosystems associated with high biodiversity in the Mediterranean region. For comparison it the same experiments have been made in two shallow-water Arctic sponge species from White Sea: Halisarca dujardini and Leucosolenia complicata. This study is the first to integrate ecological and cytological factors, and to compare different temperatures for recovery rate. It showed that:
- There is no remarkable relationship between the recovery capacity and temperature for these Mediterranean species, nor between recovery and ecological conditions.
- The rate of recovery was higher for Arctic littoral species than for Mediterranean species
- This difference in recovery rate is not due to the temperature difference but probably due to hydrological conditions. It may be due to evolution mechanisms under unstable conditions.
It is hypothesised that the mode and rate of regeneration do not depend on the growth form but on the anatomical structure of the sponges.